JavaScript基础
JavaScript 是 Web 的主流编程语言,可以实现网页与用户的动态交互。所有HTML页面都可以使用JS。
JS的导入方式
在HTML中,使用<script>标签来导入JS命令。有两种方式:
- 内部导入:在HTML中直接使用
<script>标签 + 内容。
- 外部导入:在HTML中使用
<script src="xxx.js"></script>导入外部.js文件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>js 基础</title>
<script>
console.log("js内部导入:head")
</script>
<script src="./js/hello.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
console.log("js内部导入:body")
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
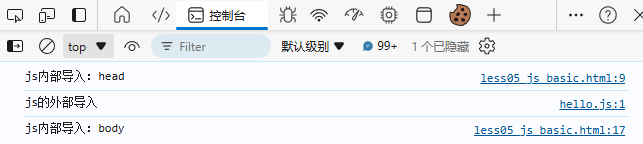
在浏览器中按F12在控制台中可以看到log:
JS基本语法
下面一个例子演示JS基本语法 (注释语法:JS中 // 注释 或/* 注释 */,CSS中为 /* 注释 */,HTML中为 <!-- 注释 -->)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>js 基础语法</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var x = 1
let y = 2
const NUM = 15
s = "a string"
v1 = null
var v2
console.log(x,y,s,NUM);
console.log(v1);
console.log(v2);
if(y == 1){
console.log("if 分支1");
}else{
console.log("if 分支2");
}
i = 0;
while(i<5){
console.log("while 循环 i=",i);
i++;
}
j = 0
while(true){
if(j==2){
console.log("continue");
j++
continue
}
if(j>=4){
console.log("break");
break
}
console.log("while 循环 j=",j);
j++;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
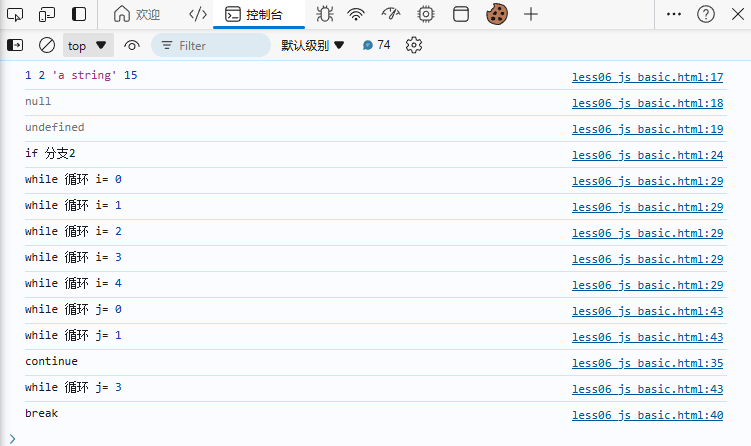
后台输出:
JS函数与事件
事件是JS的触发机制,是发生在 HTML 元素上的事情,每一个事件背后可以触发一个或多个动作。
事件绑定的方式有三种:
- HTML属性
- DOM属性
- addEventListener方法
常见的HTML属性事件有:
- onClick:点击
- onFocus:光标聚集
- onBlur:光标移开
- onMouseOver:鼠标经过
- onMouseOut:鼠标移出
- onChange:文本内容改变
- onSelect:文本框选中
示例代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>js 函数与事件</title>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="fun_onClick()">OK</button>
<br></br>
<button onfocus="fun_onFocus()" onblur="fun_blur()">Yes</button>
<script>
function fun1(input1) {
console.log("fun1");
return input1 + 1;
}
let a = fun1(1);
console.log(a);
let i = 1
function fun_onClick() {
console.log("点击按钮,次数:",i);
i++;
}
let j = 0
function fun_onFocus() {
j++;
console.log("聚集,次数:",j);
}
function fun_blur() {
j--;
console.log("聚集,次数:",j);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
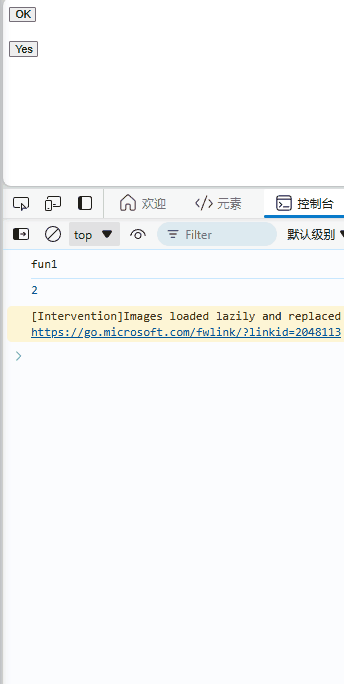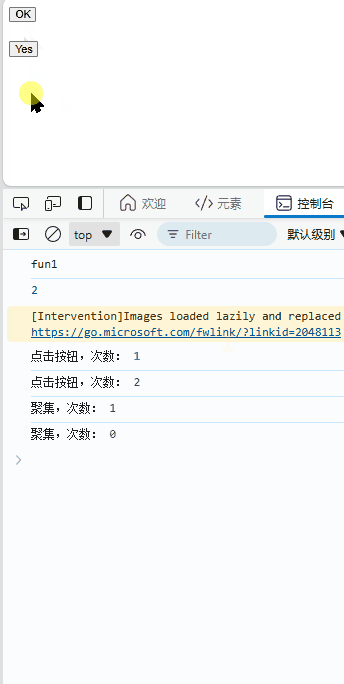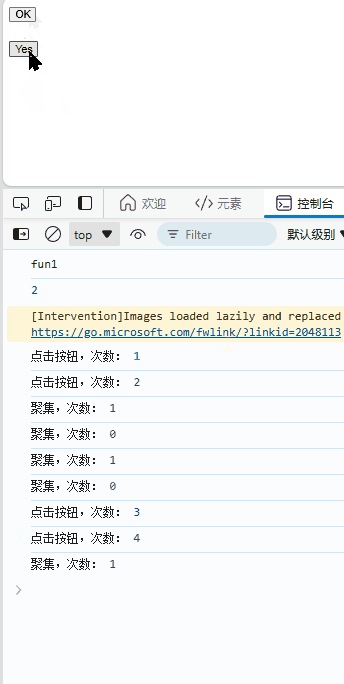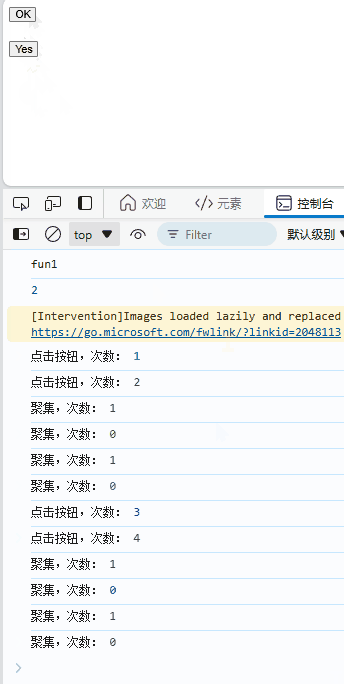
效果:
DOM 和 addListener
加载网页时,浏览器会自动创建页面的DOM:文档对象模型(Document Object Model)
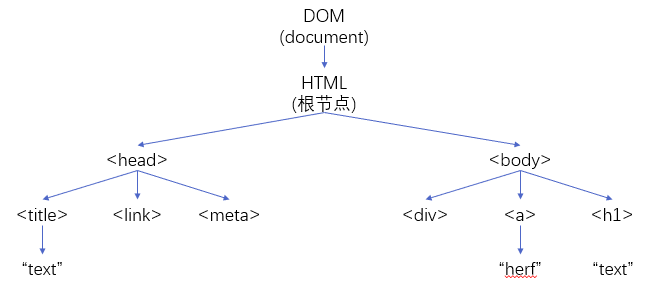
通过DOM,JS可以方便地获取HTML文档中的所有元素及其属性,再使用元素.addListener(event, action)可以对特定的元素添加“事件-动作”对,实现HTML网页的动态交互。
示例代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>js 函数与事件</title>
</head>
<body>
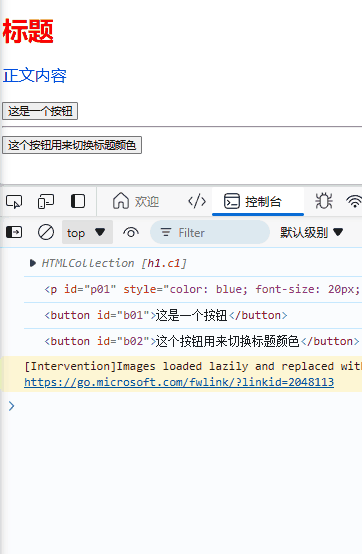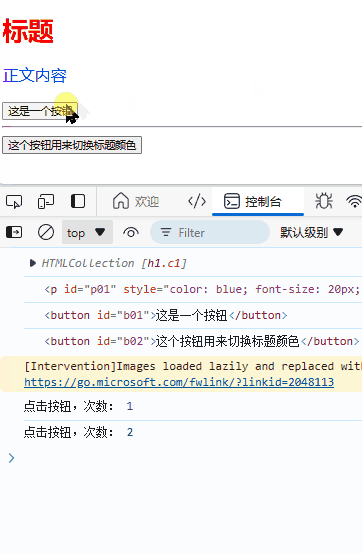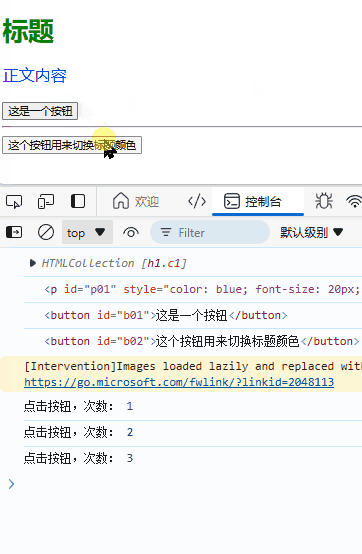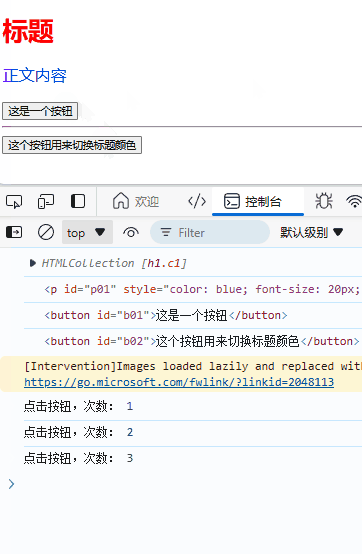
<h1 class="c1">标题</h1>
<p id="p01">正文内容</p>
<button id="b01">这是一个按钮</button>
<hr>
<button id="b02">这个按钮用来切换标题颜色</button>
<script>
var e1 = document.getElementsByClassName("c1")
var e2 = document.getElementById("p01")
var e3 = document.getElementById("b01")
var e4 = document.getElementById("b02")
console.log(e1);
console.log(e2);
console.log(e3);
console.log(e4);
e1[0].style.color = "red"
e2.style.color = "blue"
e2.style.fontSize = "20px"
e3.addEventListener("click", fun_onClick)
e4.addEventListener("click", switch_head_color)
let i = 1;
function fun_onClick() {
console.log("点击按钮,次数:",i);
i++;
}
color_set = ['red','green','blue'];
let j = 0;
function switch_head_color() {
j++;
if(j>=3)
j = j - 3
e1[0].style.color = color_set[j];
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
效果: